
Instead, a virtual network interface (similar to a loopback interface) is created on the host, providing connectivity among virtual machines and the host. This can be used to create a network containing the host and a set of virtual machines, without the need for the host's physical network interface. This can be used to create a different kind of software-based network which is visible to selected virtual machines, but not to applications running on the host or to the outside world.

The Network Address Translation (NAT) service works in a similar way to a home router, grouping the systems using it into a network and preventing systems outside of this network from directly accessing systems inside it, but letting systems inside communicate with each other and with systems outside using TCP and UDP over IPv4 and IPv6. The NAT network is a new NAT flavour introduced in VirtualBox 4.3. Please note that there are certain limitations when using Windows file sharing (see Section 6.3.3, “NAT limitations” for details).īelow diagram shows the port forwarding concept. If all you want is to browse the Web, download files and view e-mail inside the guest, then this default mode should be sufficient for you, and you can safely skip the rest of this section. This way it is possible to "pull" the virtual Ethernet cable and disrupt the connection, which can be useful to inform a guest operating system that no network connection is available and enforce a reconfiguration. In this mode, VirtualBox reports to the guest that a network card is present, but that there is no connection - as if no Ethernet cable was plugged into the card.

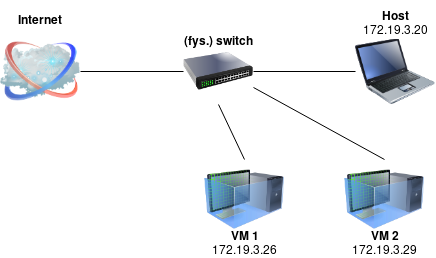
Virtualbox VM networking options are as listed below:


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
